Direct Speech
In direct speech, we convey the message of the speaker in his own actual words without any change to another person.
Indirect Speech
In indirect speech, we convey the message of the speaker in our own words to another person.
Procedure of changing direct speech into indirect speech
- Remove comma and inverted commas.
- Put "that" between the reporting and reported speeches.(it is optional to put "that" between the reporting and reported speech)
- Change the 1st letter of reported speech into small letter except for "I"
- Change the pronoun of the direct speech according to the rules described in table 2
- Change the tense of the direct speech appropriately according to rules described in table 3.
- Change the words expressing nearness in time or places of the direct speech into its appropriate words expressing distance as per table 1
Rules for changing Direct into Indirect Speech
- The past tense is often used when it is uncertain if the statement is true or when we are reporting objectively.
Indirect Speech Conversion Direct Speech Condition Present Tenses in the Direct Speech are changed into Past Tense. If the reporting or principal verb is in the Past Tense. Do Not Change Tense of reported Speech in Indirect Speech sentence If in direct speech you find say/says or will say. Direct speech the words within the quotation marks talk of a universal truth or habitual action. The reporting verb is in a present tense. - When there are two sentences combined with the help of a conjunction and both sentences have got different tenses. then change the tenses of both sentences according to the rule.
- Words expressing nearness in time or places are generally changed into words expressing distance.
Change of place and time Direct Speech Word Indirect Speech Word Here There Today that day this morning that morning Yesterday the day before Tomorrow the next day next week the following week next month the following month Now Then Ago Before Thus So Last Night the night before This That These Those Hither Thither Hence Thence Come Go
- The past tense is often used when it is uncertain if the statement is true or when we are reporting objectively.
Change in Pronouns
The pronouns of the Direct Speech are changed where necessary, according to their relations with the reporter and his hearer, rather than with the original speaker. If we change direct speech into indirect speech, the pronouns will change in the following ways.
Rules Direct Speech Indirect Speech The first person of the reported speech changes according to the subject of reporting speech. She says, "I am in tenth class." She says, "I am in tenth class." The second person of reported speech changes according to the object of reporting speech. He says to them, "You have completed your job." He tells them that they have completed their job. The third person of the reported speech doesn't change. She says, "She is in tenth class." She says that she is in tenth class. Change in Tenses
The past perfect and past perfect continuous tenses do not change.
Rules Direct Speech Indirect Speech Simple Present Changes
To
Simple Past"I always drink coffee", she said She said that she always drank coffee. Present Continuous Changes
To
Past Continuous"I am reading a book", he explained. He explained that he was reading a book Present Perfect Changes
To
Past PerfectShe said, "He has finished his work" She said that he had finished his work. Present Perfect Continuous Changes
To
Past Perfect Continuous"I have been to Spain", he told me. He told me that he had been to Spain. Simple Past Changes
To
Past Perfect"Bill arrived on Saturday", he said. He said that Bill had arrived on Saturday Past Perfect Changes
To
Past Perfect (No Change In Tense)"I had just turned out the light," he explained. He explained that he had just turned out the light. Past Continuous Changes
To
Past Perfect Continuous"We were living in Paris", they told me. They told me that they had been living in Paris. Future Changes
To
Present Conditional"I will be in Geneva on Monday", he said He said that he would be in Geneva on Monday. Future Continuous Changes
To
Conditional ContinuousShe said, "I'll be using the car next Friday." She said that she would be using the car next Friday. Changes in Modals
Rules Direct Speech Indirect Speech CAN changes into COULD He said, "I can drive a car". He said that he could drive a car. MAY changes into MIGHT He said, "I may buy a computer" He said that he might buy a computer. MUST changes into HAD TO He said, "I must work hard" He said that he had to work hard. These Modals Do Not Change: Would, could, might, should, ought to. Would They said, "we would apply for a visa" They said that they would apply for visa. Could He said, "I could run faster" He said that he could run faster. Might John said, "I might meet him". John said that he might meet him. Should He said, "I should avail the opportunity" He said that he should avail the opportunity. Ought to He said to me, "you ought to wait for him" He said to me that I ought to wait for him. Changes for Imperative Sentences
Imperative sentences consist any of these four things:
- Order
- Request
- Advice
- Suggestion
Most commonly used words to join clauses together are ordered, requested, advised and suggested. Forbid(s)/ forbade is used for the negative sentences.
Mood of Sentence in Direct Speech Reporting verb in indirect verb Order ordered Request requested / entreated Advice advised / urged Never told, advised or forbade (No need of "not" after "forbade") Direction directed Suggestion suggested to Warning warn (If a person is addressed directly) called Exclamatory Sentences
Exclamatory sentences expresses emotions. Interjections such as Hurrah, wow, alas, oh, ah are used to express emotions. The word "that" is used as join clause.
Rules for conversion of Exclamatory Direct Speech Sentences into Indirect Speech Sentences
- Exclamatory sentence changes into assertive sentence.
- Interjections are removed.
- Exclamation mark changes into full stop.
- W.H words like , "what" and "how" are removed and before the adjective of reported speech we put "very"
- Changes of "tenses" , "pronouns" and "adjectives" will be according to the previous rules.
Mood of Sentence in Direct Speech Reporting verb in indirect verb sorrow in reported speech Exclaimed with sorrow/ grief/ exclaimed sorrowfully or cried out happiness in reported speech exclaimed with joy/ delight/ exclaimed joyfully surprise in reported speech exclaimed with surprise/ wonder/ astonishment" appreciation and it is being expressed strongly applauded Interrogative Sentences
Interrogative sentences are of two types:
- Interrogative with auxiliaries at the beginning.
- Interrogatives with who, where, what, when, how etc., i.e. wh questions.
Rules for conversion of Interrogative Direct Speech Sentence into Indirect Speech Sentences
There are some rules to change direct to Indirect speech of Interrogative sentence:
RULES Changes Direct Speech Condition Indirect Speech Condition Reporting Verb said/ said to Asked, enquired or demanded. Joining Clause If sentence begins with auxiliary verb joining clause should be if or whether. If sentence begins with "wh" questions then no conjunction is used as "question-word" itself act as joining clause. Punctuation Question Mark Full Stop Helping Verbs sentences is expressing positive feeling do/does is removed from sentence. if 'No' is used in interrogative sentences do/does is changed into did. Did or has/have Had
- Helping verbs (is, am, are, was, were) are used after the subject.
- Adverbs and pronouns are converted according to the table 1 and table 2 respectively.
Punctuation in Direct Speech
In direct speech, various punctuation conventions are used to separate the quoted words from the rest of the text: this allows a reader to follow what's going on.
Here are the basic rules:RULES EXAMPLES The words that are actually spoken should be enclosed in inverted commas 'He's very clever, you know.' Start new paragraph every time when a new speaker says something. 'They think it's a more respectable job,' said Joe.
'I don't agree,' I repliedComma, full stop, question mark, or exclamation mark must be present at the end of reported sentences. This is placed inside the closing inverted comma or commas. 'Can I come in?' he asked.
'Just a moment!' she shouted.
'You're right,' he said.If direct speech comes after the information about who is speaking, comma is used to introduce the piece of speech, placed before the first inverted comma. Steve replied, 'No problem.' If the direct speech is broken up by information about who is speaking, comma (or a question mark or exclamation mark) is used to separate the two reported speech 'You're right,' he said. 'It feels strange.'
'Thinking back,' she said, 'he didn't expect to win.'Rules for conversion of Indirect Speech to Direct Speech
To change from Indirect to Direct Speech, keep the rules of the Direct Speech are applied in the reverse order.
- Use the reporting verb, "say" or "said to" in its correct tense.
- Remove the conjuctions "that, to, if or whether etc". wherever necessary.
- Insert quotation marks, question mark, exclamation and fullstop, wherever necessary.
- Put a comma before the statement.
- Write the first word of the statement with capital letter.
- Change the past tense into present tense wherever the repoting verb is in the past tense.
- Convert the past perfect either into past tense or present perfect as found necessary.
- Be careful about the order of words in the question.
The following table will enable to find the kind of sentence:
Indirect (Conjunction) Direct (Kind of Sentence) That Statement (or) Exclamatory sentence to, not to Imperative requested + to Begin the imperative sentence with "please" if or whether Interrogative sentence (Helping Verb + Subject + Main Verb + ...?) What, When, How etc., (Wh or How + Helping Verb + Subject + Main Verb + ...?)
Source: http://cdac.olabs.edu.in/?sub=84&brch=26&sim=219&cnt=1
100 Examples:
100 Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech in English, 100 Examples of reported speech in english;
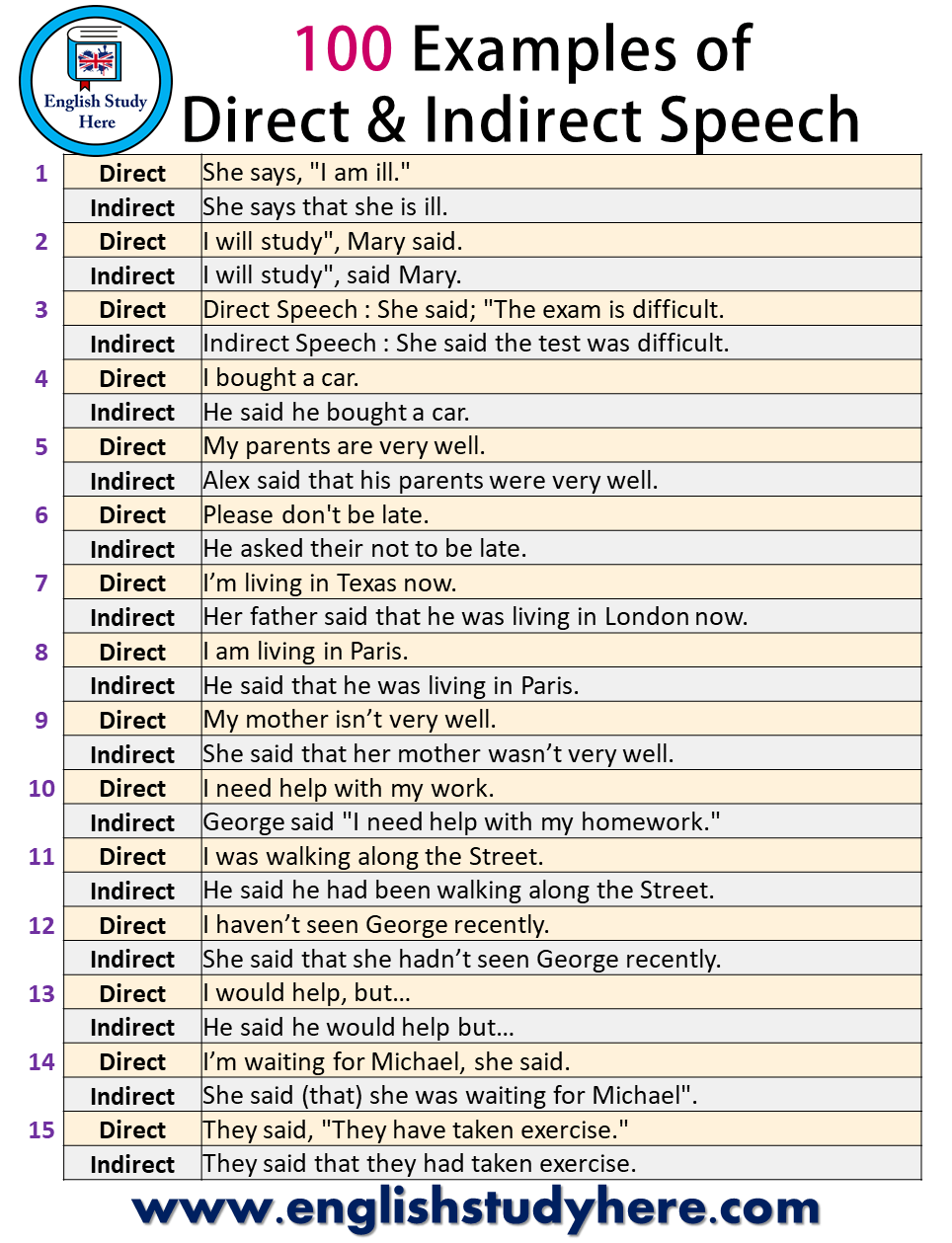
| 1 | Direct | She says, “I am ill.” |
| Indirect | She says that she is ill. | |
| 2 | Direct | I will study”, Mary said. |
| Indirect | I will study”, said Mary. | |
| 3 | Direct | She said; “The exam is difficult. |
| Indirect | She said the test was difficult. | |
| 4 | Direct | I bought a car. |
| Indirect | He said he bought a car. | |
| 5 | Direct | My parents are very well. |
| Indirect | Alex said that his parents were very well. | |
| 6 | Direct | Please don’t be late. |
| Indirect | He asked their not to be late. | |
| 7 | Direct | I’m living in Texas now. |
| Indirect | Her father said that he was living in London now. | |
| 8 | Direct | I am living in Paris. |
| Indirect | He said that he was living in Paris. | |
| 9 | Direct | My mother isn’t very well. |
| Indirect | She said that her mother wasn’t very well. | |
| 10 | Direct | I need help with my work. |
| Indirect | George said “I need help with my homework.” | |
| 11 | Direct | I was walking along the Street. |
| Indirect | He said he had been walking along the Street. | |
| 12 | Direct | I haven’t seen George recently. |
| Indirect | She said that she hadn’t seen George recently. | |
| 13 | Direct | I would help, but… |
| Indirect | He said he would help but… | |
| 14 | Direct | I’m waiting for Michael, she said. |
| Indirect | She said (that) she was waiting for Michael”. | |
| 15 | Direct | They said, “They have taken exercise.” |
| Indirect | They said that they had taken exercise. |

| 16 | Direct | I can speak perfect Spanish. |
| Indirect | He said he could speak perfect Spanish. | |
| 17 | Direct | I haven’t seen Mary. |
| Indirect | He said he hadn’t seen Mary. | |
| 18 | Direct | What is your name? she asked me. |
| Indirect | She asked me what my name was. | |
| 19 | Direct | I was sleeping when Mary called. |
| Indirect | He said that he had been sleeping when Mary called. | |
| 20 | Direct | Please help me! |
| Indirect | He asked me to help his. | |
| 21 | Direct | It is too late. |
| Indirect | I said it was too late. | |
| 22 | Direct | I had taken Spanish lessons before. |
| Indirect | He said he had taken Spanish lessons before. | |
| 23 | Direct | Did you do your homework? |
| Indirect | He asked me if I did (had done) my homework. | |
| 24 | Direct | Please help me carry this! |
| Indirect | My mother asked me to help her carry that. | |
| 25 | Direct | I like ice cream. |
| Indirect | He said that he liked ice cream. | |
| 26 | Direct | I’II see you later. |
| Indirect | He said he would see me later. | |
| 27 | Direct | I could swim when I was four. |
| Indirect | He said he could swim when he was four. | |
| 28 | Direct | I should call my mother. |
| Indirect | He said he should call her mother. | |
| 29 | Direct | I might be late. |
| Indirect | He said he might be late. | |
| 30 | Direct | He said, “I was teaching earlier.” |
| Indirect | He said he had been teaching earlier. |

| 31 | Direct | Mary said, “I have been writing this essay.” |
| Indirect | Mary said that he had been writing that essay. | |
| 32 | Direct | Michael said, “I may go there.’ |
| Indirect | Michael says that she may go there. | |
| 33 | Direct | We can´t go the zoo next week. |
| Indirect | They said they couldn’t go to the zoo next week. | |
| 34 | Direct | George is said, “I write a letter”. |
| Indirect | George is said that she wrote a letter. | |
| 35 | Direct | I said, “He is driving a car” |
| Indirect | I said that he was driving a car. | |
| 36 | Direct | I am reading a book, he explained. |
| Indirect | He explained that he was reading a book. | |
| 37 | Direct | My father said, “I am cooking dinner.” |
| Indirect | My father said he was cooking dinner. | |
| 38 | Direct | My sister said, “I had already eaten.” |
| Indirect | My sister said she had already eaten. | |
| 39 | Direct | My boyfriend asked, “Do you like horror films?” |
| Indirect | Do you like horror films? my boyfriend asked. | |
| 40 | Direct | I never get up late, my mother said. |
| Indirect | My mother said that she never got up late. | |
| 41 | Direct | She said, “I might come early.” |
| Indirect | She said she might come early. | |
| 42 | Direct | I am leaving home now.” |
| Indirect | He said that he left home then. | |
| 43 | Direct | Are you living here? |
| Indirect | He asked me if I was living here. | |
| 44 | Direct | I’m going to come. |
| Indirect | She said that she was going to come. | |
| 45 | Direct | We can communicate smoothly. |
| Indirect | They said that they could communicate smothly. |
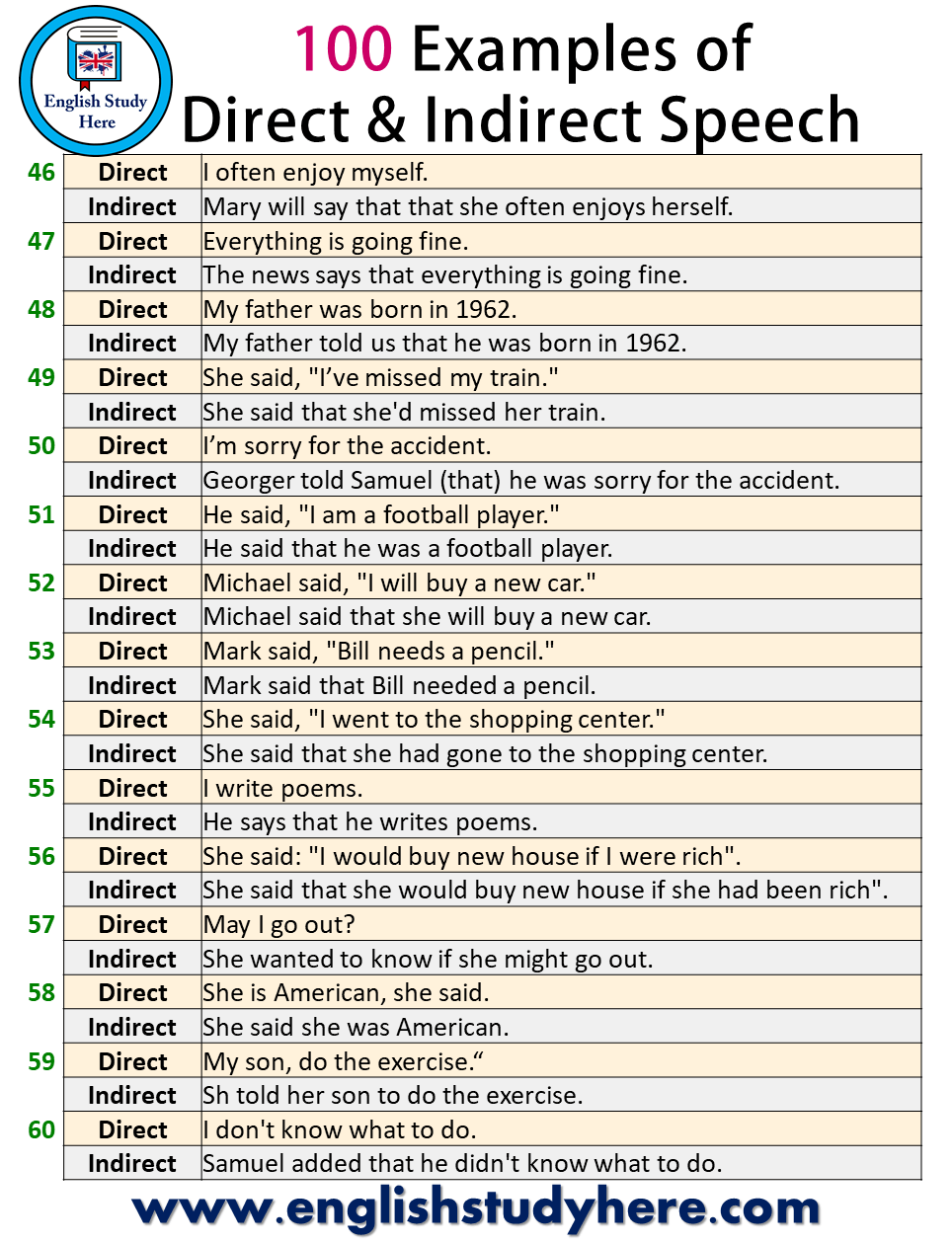
| 46 | Direct | I often enjoy myself. |
| Indirect | Mary will say that that she often enjoys herself. | |
| 47 | Direct | Everything is going fine. |
| Indirect | The news says that everything is going fine. | |
| 48 | Direct | My father was born in 1962. |
| Indirect | My father told us that he was born in 1962. | |
| 49 | Direct | She said, “I’ve missed my train.” |
| Indirect | She said that she’d missed her train. | |
| 50 | Direct | I’m sorry for the accident. |
| Indirect | Georger told Samuel (that) he was sorry for the accident. | |
| 51 | Direct | He said, “I am a football player.” |
| Indirect | He said that he was a football player. | |
| 52 | Direct | Michael said, “I will buy a new car.” |
| Indirect | Michael said that she will buy a new car. | |
| 53 | Direct | Mark said, “Bill needs a pencil.” |
| Indirect | Mark said that Bill needed a pencil. | |
| 54 | Direct | She said, “I went to the shopping center.” |
| Indirect | She said that she had gone to the shopping center. | |
| 55 | Direct | I write poems. |
| Indirect | He says that he writes poems. | |
| 56 | Direct | She said: “I would buy new house if I were rich”. |
| Indirect | She said that she would buy new house if she had been rich”. | |
| 57 | Direct | May I go out? |
| Indirect | She wanted to know if she might go out. | |
| 58 | Direct | She is American, she said. |
| Indirect | She said she was American. | |
| 59 | Direct | My son, do the exercise.“ |
| Indirect | Sh told her son to do the exercise. | |
| 60 | Direct | I don’t know what to do. |
| Indirect | Samuel added that he didn’t know what to do. |

| 61 | Direct | The Minister said, “There will be no growth this year.” |
| Indirect | The Minister said that there will be no growth this year. | |
| 62 | Direct | I’m sitting on the chair. |
| Indirect | Arya said that she was sitting on the chair. | |
| 63 | Direct | “I’ve found a new job,” my mother said. |
| Indirect | My mother said that she had found a new job. | |
| 64 | Direct | Go to bed! mother said to the children. |
| Indirect | Mother told the children to go to bed. | |
| 65 | Direct | Mark arrived on Sunday, he said. |
| Indirect | He said that Mark had arrived on Sunday. | |
| 66 | Direct | I have been to France, she told me. |
| Indirect | She told me that she had been to France. | |
| 67 | Direct | Michael said, “I have finished my lunch.” |
| Indirect | She said that she had finished his lunch. | |
| 68 | Direct | My brother said, “I met Alex yesterday.’ |
| Indirect | My brother said that he had met Alex yesterday. | |
| 69 | Direct | The dentist said, “Your father doesn’t need an operation.” |
| Indirect | Dentist said that my father doesn’t need an operation. | |
| 70 | Direct | He said, “Man is mortal.” |
| Indirect | He said that man is mortal. | |
| 71 | Direct | Sansa said “I am very busy now”. |
| Indirect | Sansa said that she was very busy then. | |
| 72 | Direct | He said, “I like coffee.” |
| Indirect | He said (that) he likes coffee. | |
| 73 | Direct | Come at 11! |
| Indirect | Alex told me to come at 11. | |
| 74 | Direct | He said, “he is listening to the music” |
| Indirect | He said that he was listening to the music. | |
| 75 | Direct | Mercedes is a good car. |
| Indirect | Tom said Mercedes was a good car. |
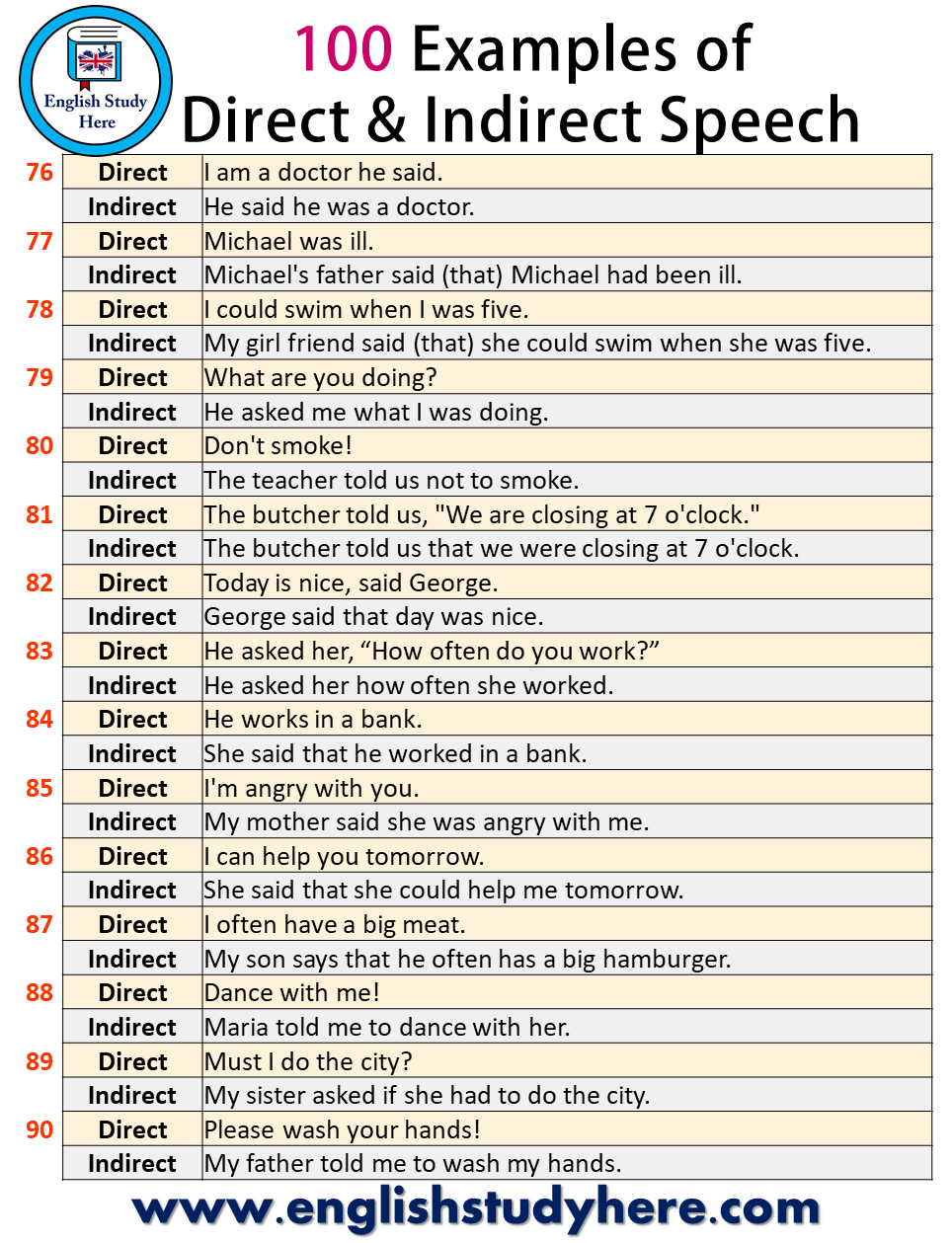
| 76 | Direct | I am a doctor he said. |
| Indirect | He said he was a doctor. | |
| 77 | Direct | Michael was ill. |
| Indirect | Michael’s father said (that) Michael had been ill. | |
| 78 | Direct | I could swim when I was five. |
| Indirect | My girl friend said (that) she could swim when she was five. | |
| 79 | Direct | What are you doing? |
| Indirect | He asked me what I was doing. | |
| 80 | Direct | Don’t smoke! |
| Indirect | The teacher told us not to smoke. | |
| 81 | Direct | The butcher told us, “We are closing at 7 o’clock.” |
| Indirect | The butcher told us that we were closing at 7 o’clock. | |
| 82 | Direct | Today is nice, said George. |
| Indirect | George said that day was nice. | |
| 83 | Direct | He asked her, “How often do you work?” |
| Indirect | He asked her how often she worked. | |
| 84 | Direct | He works in a bank. |
| Indirect | She said that he worked in a bank. | |
| 85 | Direct | I’m angry with you. |
| Indirect | My mother said she was angry with me. | |
| 86 | Direct | I can help you tomorrow. |
| Indirect | She said that she could help me tomorrow. | |
| 87 | Direct | I often have a big meat. |
| Indirect | My son says that he often has a big hamburger. | |
| 88 | Direct | Dance with me! |
| Indirect | Maria told me to dance with her. | |
| 89 | Direct | Must I do the city? |
| Indirect | My sister asked if she had to do the city. | |
| 90 | Direct | Please wash your hands! |
| Indirect | My father told me to wash my hands. |

| 91 | Direct | Michael asked Tom, “Are you married?” |
| Indirect | Michael asked Tom whether she was married. | |
| 92 | Direct | I didn’t go to the party. |
| Indirect | Alex said that he hadn’t gone to the party. | |
| 93 | Direct | He said, “I live in the city center.” |
| Indirect | He said he lived in the city center. | |
| 94 | Direct | My father is helping me study. |
| Indirect | He said his father was helping his study. | |
| 95 | Direct | He said, “I can swim.” |
| Indirect | He said he could swim. | |
| 96 | Direct | He said “I had lived in Paris.” |
| Indirect | He said that she had lived in Paris. | |
| 97 | Direct | I don’t understand you. |
| Indirect | Teacher said that he didn’t understand me. | |
| 98 | Direct | He said, “I will wash my teeth”. |
| Indirect | He said he would wash his teeth. | |
| 99 | Direct | Why are you going to school? |
| Indirect | Mary asked Alex why he was going to school. | |
| 100 | Direct | Listen to me! |
| Indirect | Mother told me to listen to him. Source: https://englishstudyhere.com/reported-speech/100-examples-of-direct-and-indirect-speech/ |






No comments:
Post a Comment